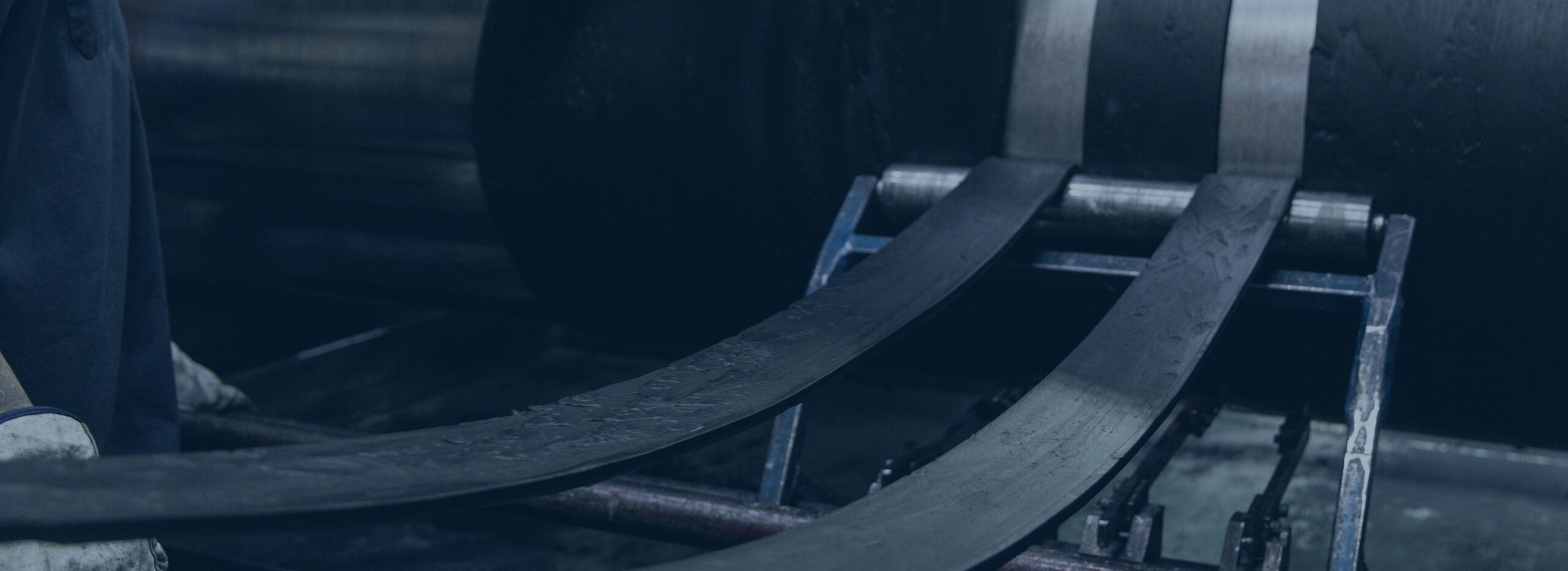
Neoprene, a trademarked name for polychloroprene (or CR rubber), is a versatile synthetic elastomer prized for its balance of mechanical strength, chemical stability, and weather resistance. Widely used in industrial, automotive, and consumer products, neoprene compounds offer a dependable solution for applications requiring durability in harsh environments.
Through advanced neoprene rubber formulation techniques, these rubber compounds can be tailored to meet precise performance criteria.
What is Neoprene Rubber?
Neoprene is a synthetic rubber derived from the polymerization of chloroprene. Its chemical structure gives it resistance to oil, weathering, ozone, and moderate levels of heat and chemicals. As a CR rubber compound, neoprene offers excellent physical toughness, making it suitable for both static and dynamic sealing, gasketing, and insulation applications.
Key Properties of Neoprene Compounds
The value of a neoprene compound lies in its well-rounded performance across a range of environments. Compound formulations can be optimized for strength, elasticity, flame resistance, or environmental exposure.
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Withstands moderate exposure to oils, greases, and chemicals |
| Weather and Ozone Resistance | Performs reliably in outdoor and UV-prone environments |
| Flame Resistance | Inherently self-extinguishing, making it suitable for safety-critical applications |
| Mechanical Strength | Offers good tensile and tear resistance in dynamic conditions |
| Flexibility | Remains pliable in cold temperatures; resists cracking and shrinkage |
| Adhesion | Bonds well to metals, textiles, and other substrates for coated products |
Applications of Neoprene Rubber Compounds
- Automotive: Engine mounts, seals, belts, and hoses rely on neoprene for its vibration damping and fluid resistance.
- Industrial Sealing: Gaskets, O-rings, and sleeves benefit from neoprene’s resilience to pressure, temperature shifts, and exposure to oils or coolants.
- Wire & Cable Insulation: Neoprene’s flame resistance and flexibility make it ideal for jackets and sheathing in harsh electrical environments.
- Construction & HVAC: Used in expansion joints, weather seals, and insulation pads to absorb movement and block moisture or air infiltration.
- Consumer Products: Neoprene is found in wetsuits, orthopedic braces, and protective gear due to its softness, stretch, and temperature insulation.
Customizing Neoprene Rubber Formulations
A neoprene rubber formulation can be engineered to meet specific mechanical, chemical, or thermal requirements. This is achieved by adjusting core ingredients and additives within the compound.
- Cure Systems – Peroxide and metal oxide curing affect elasticity, thermal resistance, and compression set.
- Plasticizers – Improve flexibility and cold temperature performance without sacrificing flame resistance.
- Fillers – Carbon black, silica, or calcium carbonate can modify strength, cost, or density.
- Special Additives – Fire retardants, antioxidants, and anti-cracking agents extend the compound’s lifespan and safety compliance.
Advancements in Neoprene Compound Technology
- Low-Temperature Grades: New formulations remain flexible and durable even in extreme cold, expanding neoprene’s usability in arctic or refrigerated environments.
- Flame-Retardant Blends: Modern CR rubber compounds are enhanced to meet stricter fire safety standards in automotive, mass transit, and aerospace applications.
- Eco-Conscious Alternatives: Formulators are developing bio-based plasticizers and recyclable neoprene blends to reduce environmental impact without compromising performance.
- Multi-Polymer Blends: Neoprene is often blended with EPDM, nitrile, or natural rubber to balance cost, processability, and application-specific performance.
- Nanostructured Rubber: Incorporating nanoparticles into neoprene improves mechanical strength and thermal stability. This allows neoprene to be used in more demanding applications.